service items
European certification
Introduction to EU ErP Directive (2009/125/EC)
To improve the environmental performance of energy-consuming products and control environmental pollution. On October 31, 2009, the European Union officially issued the Ecological Requirements Directive 2009/125/EC for energy-related products, namely the ErP (Energy-related Products) Directive "The Directive to Establish a Framework for the Eco-design Requirements for Energy-Related Products". It is a rewrite of the EuPhoria (Energy-using Products) Directive (2005/32/EC) and further expands its scope. From November 20, 2009, the ErP Directive 2009/125/EC replaced the original EuP Directive (2005/32) /EC, 2008/28/EC).
The IM that was originally based on the EuP instruction will be converted to the IM of this instruction at the same time.

Compared with the EuP Directive, the main change between the ErP Directive and the EuP Directive is the expansion of Energy-using Products in the original EuP Directive into Energy-related Products, which expands the scope of the EuP Directive. Energy-related products refer to products that will affect energy consumption when they are placed on the EU market and/or put into use; or their environmental performance can be independently assessed for parts intended to be assembled on products covered by this directive. In addition to the energy-consuming products covered by the original EuP Directive, it also includes other energy-saving products, such as windows, insulation materials or water products (such as shower heads, faucets, etc.). Like EuP, the ErP directive does not apply to the transportation of people and goods.
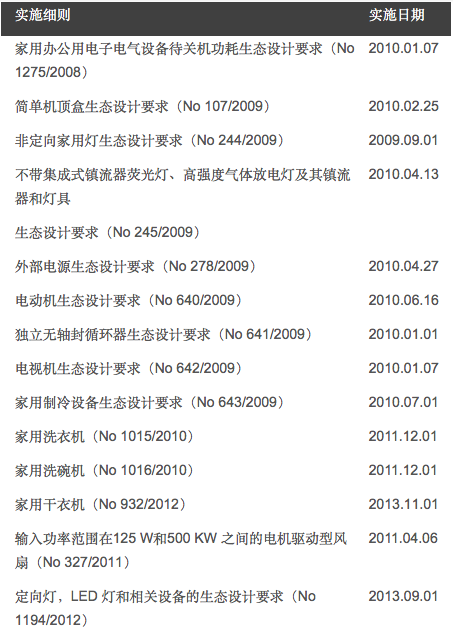
The ErP directive is not a directive directed at product requirements, but a framework directive. In accordance with the relevant provisions of this directive, the European Union has further formulated directives on eco-design requirements for certain types of energy-consuming products, called "Implementing Measures", or IM for short. The implementation rules that have been promulgated and implemented are as follows:
Basic steps of ErP certification
1. Compliance Assessment
According to the requirements of the ErP Directive, the manufacturer can "internal design control" (ErP Directive Annex IV) or "Environmental Management System"
(ErP instruction Annex V) Choose one of the two evaluation modes for evaluation.
2. Organize and form technical documents (TDF)
The manufacturer must form a technical document
Technical documentation should include information on design, manufacturing, operation and final product disposal
The details will be clarified through the implementation measures of each product
3. Issue a Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
Basic Information
Follow the instructions and standards
4. Label with CE mark
Harmonized standard test (EMC, LVD, etc.)
Labeling CE mark
ERP EU energy efficiency certification (Figure 3)
service
Make a reasonable evaluation of the product eco-design, and issue an authoritative ErP eco-design evaluation report and certificate. The products are tested according to the ErP implementation rules, and authoritative IM reports and certificates are issued.






 telephone:
telephone: Phone:
Phone: Email:
Email: Address:
Address: